Facial recognition technology has increasingly become a central part of our daily lives, from unlocking smartphones to enhancing security measures at airports. One of the key areas where facial recognition is gaining traction is in travel documents, such as passports and visas. In this article, we’ll explore the crucial role facial recognition plays in travel document photos, how it’s changing the travel experience, and the potential challenges and benefits associated with this technology.
What is Facial Recognition Technology?
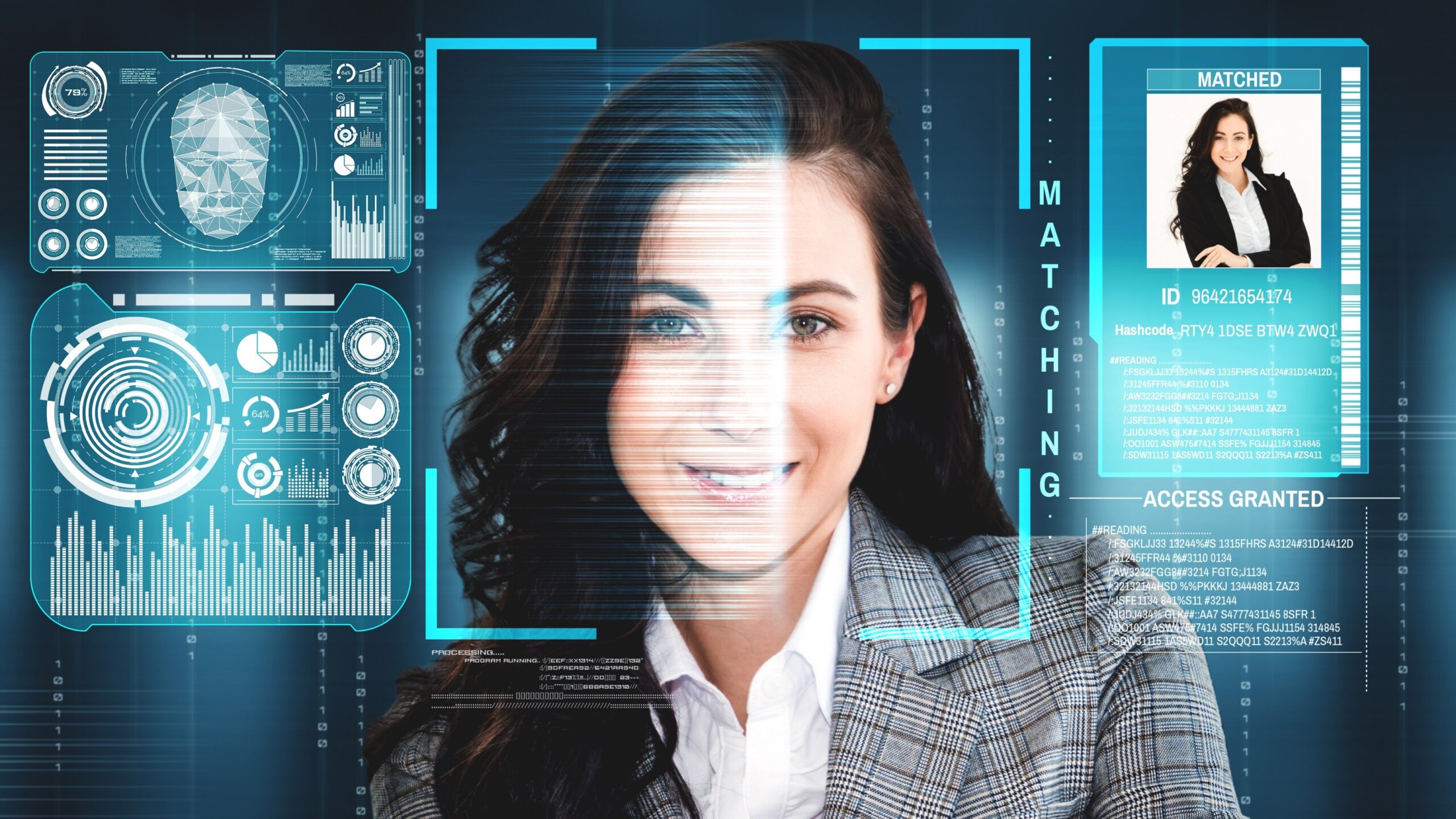
Facial recognition technology is a type of biometric identification system that plays an important role in security and identification processes. It works by analyzing and comparing the patterns in an individual’s facial features to identify or verify their identity. This technology focuses on various unique facial characteristics, such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contours of the jawline. These features are measured and stored as data, which can then be compared with a database of known facial data for identification.
This process of identification is highly effective due to the uniqueness of each individual’s face. Unlike traditional methods, facial recognition does not require physical contact or invasive procedures, making it a more convenient and non-intrusive way to confirm someone’s identity. The data points gathered from a person’s face are used to create a detailed biometric template, which is then compared with stored records, allowing for accurate identification.
When it comes to travel documents, facial recognition technology is essential for ensuring security and efficiency. For instance, when travelers apply for passports or visas, they must submit a photo of their face. This image is incorporated into the travel document and is stored in the system, enabling the document to be used for future verification. At border checkpoints, facial recognition systems can match the traveler’s face with the stored image in their passport or visa, providing an automated and secure way to verify identity.
As this technology advances, facial recognition is becoming a standard feature in many modern travel documents. The introduction of biometric passports, which contain a microchip with the traveler’s facial image and other personal details, has made it possible to streamline border control processes. These passports are now commonly used worldwide and offer benefits like faster processing times, enhanced security, and reduced risk of fraud, all while ensuring accuracy in identity verification.
The Impact of Facial Recognition on Travel Experience
| Aspect | Description | Benefits | Challenges | Examples |
| Speeding Up Border Control | Facial recognition technology allows travelers to bypass long queues at border crossings by using automated kiosks. It provides a faster, more efficient process at airports. | – Reduced wait times at passport control. – Streamlined process from check-in to boarding. – Faster border entry. |
– Requires travelers to enroll in biometric systems. – Dependence on technology could create delays in case of system malfunctions. |
– Automated border control gates in airports like Heathrow and Schiphol. – Contactless check-ins at major international airports. |
| Improved Security and Fraud Prevention | Facial recognition enhances security by verifying that the person presenting a travel document is the same person in the photograph, reducing the chances of identity fraud. | – Increased security and reduced risk of fake or stolen documents. – Greater confidence in identity verification. – Harder for travelers to forge documents. |
– Potential privacy concerns related to biometric data. – Systems may fail if there are discrepancies in photo quality or facial recognition errors. |
– Biometric passports with facial images and chips. – Facial recognition used to verify passport holders at border control in the U.S. and EU countries. |
| Increased Efficiency for Airlines and Immigration Authorities | Automated facial recognition systems make it easier for airlines and immigration authorities to verify travelers without manually checking documents, leading to quicker processes. | – Streamlined identity verification process. – Reduced workload for airline staff and immigration officers. – Faster processing at airports. |
– Implementation costs for airlines and airports. – Concerns about system reliability and potential delays. |
– Use of facial recognition for check-in and boarding at airports like Delta’s facial recognition at Atlanta Hartsfield-Jackson. – Automated border entry in Australia. |
| A More Personalized Travel Experience | Facial recognition has the potential to offer personalized services, such as quicker baggage handling, VIP lounge access, and customized recommendations based on biometric data. | – Enhanced customer experience. – Tailored services to individual preferences. – Potential for faster handling of luggage. |
– Privacy concerns related to the collection and use of biometric data. – Implementation may not be available at all airports or airlines. |
– Personalized services at airports like the “Clear” program in the U.S. – Fast-track baggage handling at select international airports. |
| Contactless Travel | Travelers can experience a fully contactless journey, from check-in to boarding, using facial recognition technology for all steps of the travel process. | – Contactless and seamless travel. – Reduced physical interactions. – Enhanced convenience for travelers. |
– Technology could be inaccessible to some travelers due to technical limitations. – Concerns about data security and breaches. |
– Use of facial recognition from check-in to boarding at airports like Singapore Changi. – Contactless immigration systems at airports like Dubai. |
Benefits of Facial Recognition in Travel Documents
- Faster Processing Times
- Travelers can move through check-in, security, and immigration with minimal delays.
- Automated systems speed up the verification process, reducing wait times.
- Improves the overall efficiency of air travel, allowing for a smoother journey.
- Better Security and Accuracy
- Facial recognition provides a more reliable and accurate method of identifying travelers.
- Reduces the likelihood of human error in the identification process.
- Enhanced security by ensuring that the person presenting the travel document is the correct individual.
- Reducing the Risk of Identity Theft
- Biometric data is much harder to duplicate or forge compared to traditional travel documents.
- Facial recognition helps to prevent the use of stolen or lost travel documents.
- Adds an extra layer of protection against fraud, ensuring the integrity of travel identification.
- Streamlined Travel Experience
- Facial recognition enables a contactless and frictionless journey from check-in to boarding.
- Reduces the need for manual document checks and long queues.
- Enhances convenience for travelers, making the process more seamless and less stressful.
Challenges and Concerns of Facial Recognition in Travel Documents
While facial recognition technology offers numerous benefits in the realm of travel documents, there are significant challenges and concerns that need to be addressed. Privacy is one of the most prominent issues. Travelers may feel uneasy knowing that their biometric data, such as facial images, is being collected, stored, and used for identification purposes. Many individuals worry about the potential misuse of this data, especially if it is stored in centralized databases that could be vulnerable to hacking or unauthorized access.
Security risks also remain a concern, despite facial recognition being considered a more secure method of identification compared to traditional travel documents. Cyberattacks and data breaches could expose sensitive biometric data, which could then be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes. These security vulnerabilities highlight the need for robust encryption methods and safeguards to protect travelers’ data from being compromised.
Another challenge lies in the accuracy of facial recognition technology, particularly when it comes to diverse populations. Studies have shown that facial recognition systems often struggle to accurately identify individuals with darker skin tones, women, and other marginalized groups. This can lead to false positives or negatives, potentially causing delays, discrimination, or unfair treatment at border control points. As the technology evolves, it is crucial to ensure that it is trained to be more inclusive and accurate across all demographics.
Finally, the cost of implementing facial recognition systems and biometric passports can be prohibitive for many countries, especially those with limited resources. The infrastructure required to support these technologies—including the installation of automated border control systems and the development of secure databases—can be expensive. As a result, some countries may face difficulties in adopting these technologies, creating disparities in the travel experiences of their citizens compared to those in countries with the financial means to implement them.
The Future of Facial Recognition in Travel Documents
| Aspect | Details | Benefits | Challenges | Future Outlook |
| Adoption by More Countries | More nations are expected to adopt facial recognition for travel documents, as its benefits become increasingly clear. Many countries are working toward biometric passports. | – Improved security and efficiency. – More streamlined travel experiences globally. |
– Variability in global adoption rates due to cost and infrastructure limitations. – Privacy concerns around global data sharing. |
The future sees wider adoption of biometric passports and a global push for universal standards in facial recognition systems. |
| Integration with Other Technologies | Facial recognition may be integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to improve efficiency and accuracy. AI could help reduce biases. | – Enhanced accuracy in identifying travelers. – Improved ability to address biases in facial recognition systems. |
– Technical challenges in integrating these systems. – Ongoing concerns over the ethical use of AI. |
The technology is expected to evolve into a more accurate and reliable system, supported by AI, which will help optimize the travel process further. |
| Increased Use of Automated Border Control | The use of automated border control systems with facial recognition is likely to grow. This reduces the need for human interaction and accelerates processing times. | – Faster border processing. – Reduced human interaction, especially in pandemic situations. |
– High initial investment for infrastructure. – Potential technical glitches with automated systems. |
As technology advances, automated border control systems will become more prevalent, offering faster, contactless experiences at checkpoints. |
Facial Recognition Technology: A Look at Global Trends
- United States and Facial Recognition
- The U.S. has integrated facial recognition technology at major airports as part of the “Biometric Entry-Exit” program.
- This program is designed to verify the identity of travelers entering and leaving the country using facial recognition.
- It aims to streamline border control processes and enhance security by automating identity verification.
- European Union’s Adoption of Biometric Passports
- The European Union has made biometric passports mandatory for all new passports issued across member states.
- These passports include facial recognition data stored in a chip, which can be used for border control and security checks.
- The use of biometric passports is becoming widespread throughout the EU, improving the efficiency and accuracy of border control processes.
- Facial Recognition in Asia
- In countries like China and Japan, facial recognition technology is utilized not only for travel documents but also for various other services.
- In China, facial recognition is widely implemented in transportation systems, payment methods, and public services.
- Japan has integrated facial recognition for improved security at airports and train stations, as well as for enhanced convenience in public services.